SPSS Tutorials: Recoding Variables
Writing back to another variable turns an original variable into a new variable. That is, the changes do not overwrite the original variable; Instead, they are applied to the copy of the original variable under a new name. To re-encode to different variables, click Transform > Recode into different variables.Reading: how to re-encode in spssThe Recode to Other Variables window will appear.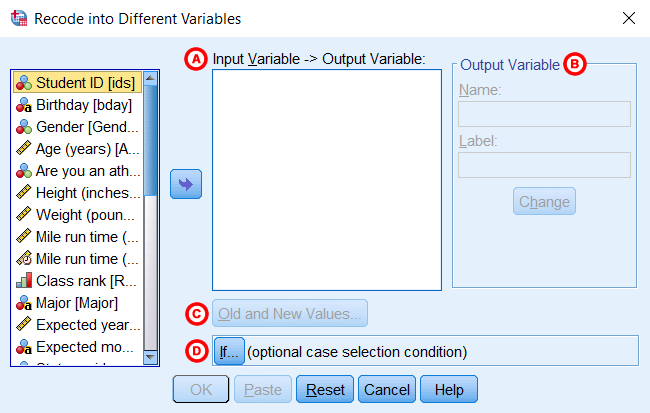
Old and new value
After you click Old and new valuea new window where you specify how to convert the values will appear.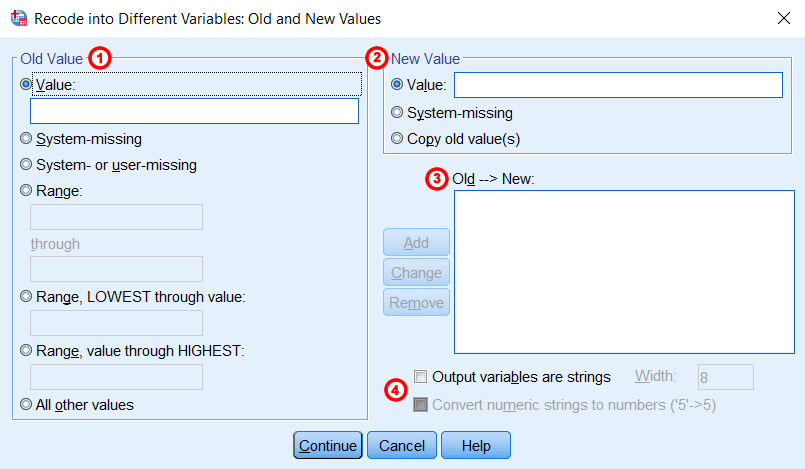
- Value: Enter a specific code that represents an existing category.
- Missing system: Applies to any system missing values (.)
- Missing system or user: Applies to any system missing values (.) or special user-defined missing value codes in the Variables View window
- Range: For use with ordered catalogs or continuous measurements. Enter the lower boundary and the upper boundary to be encoded. The encrypted catalog will include both endpoints, so data values exactly equal to the boundaries will be included in that catalog.
- Range, LOWEST to value: For use with ordered catalogs or continuous measurements. Encode all values less than or equal to a number.
- Range, value to HIGHEST: For use with ordered catalogs or continuous measurements. Encode all values greater than or equal to a number.
- All other values: Applies to any value that is not explicitly calculated by the previous coding rules. If this setting is used, it will be applied last.
2New Value: Specify a new value for your variable (i.e. a specific number such as “2”, systematic missing or duplicate old values) .3Old -> New: Once you have selected the old and new values for your selected variable in (1) and (2), click add in area (3), Old->New. The repeat code you specified will now appear in the text field. If you need to change one of the code snippets you added Old->New area section, just click on the one you want to change and make changes in (1) and (2) as needed. You will need to repeat these steps for each value that you want to re-encode. Once you have specified all the transformations that you want to perform to the selected variable, click the “Continue” button.4Output variable is string and Convert numeric string to number: These options change the variable type of the new variable.
- Output variables are strings: The new variable will be a string variable.
- Convert numeric string to number: This option can only be used when your input variable is a string and will be grayed out otherwise. If the input variable is a string, but the data values themselves are valid numbers, selecting this option will convert numeric strings to real numbers. (If any other character symbols appear in the data values, the conversion will fail, even if the numbers have different values. This includes the dollar sign and the fraction symbol. hundred.)
“If” option
Read more: how to change emoji on snapchat streak | Top Q&A Sometimes you may just want to re-encode the values for a particular variable when other conditions in your data are satisfied. This means that the cases that meet the conditions will be re-encoded and the cases that do not meet the conditions will be assigned a missing value. To specify such conditions, click If to display the Record to different variables: If case window.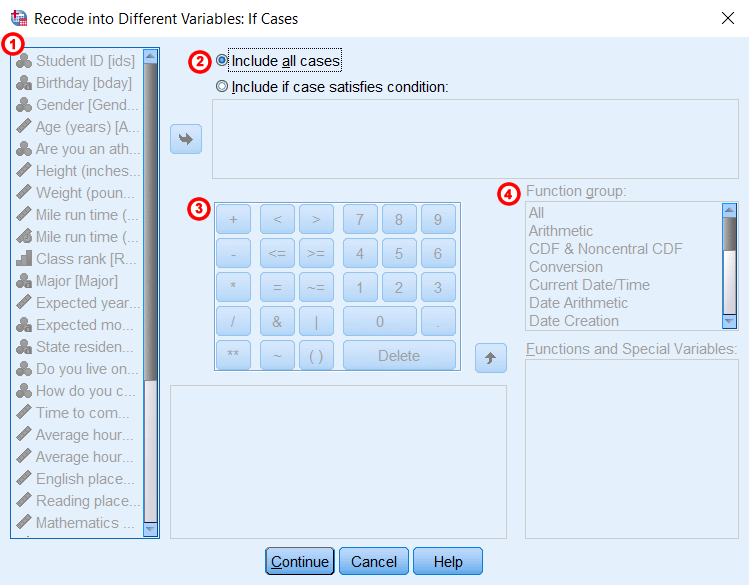
Last, Wallx.net sent you details about the topic “SPSS Tutorials: Recoding Variables❤️️”.Hope with useful information that the article “SPSS Tutorials: Recoding Variables” It will help readers to be more interested in “SPSS Tutorials: Recoding Variables [ ❤️️❤️️ ]”.
Posts “SPSS Tutorials: Recoding Variables” posted by on 2021-10-26 06:45:09. Thank you for reading the article at wallx.net