NVIDIA GTX 1080 Ti Overclocking Guide
GTX 1080 Ti Overclocking Guide: Introduction
Contents
Welcome to the NVIDIA GTX 1080 Ti Overclocking Guide! In this article, I’ll cover everything from NVIDIA’s infamous Boost 3.0 technology to practical overclocking instructions. While this mainly applies to the 1080 Ti, the core concepts and fundamentals of overclocking will apply to the GTX 1060, 1070, 1080, and Titan X/Xp, all of which belong to the same Pascal GPU family. . I suggest that, in order to get the most out of this tutorial, you should not skip it, because I refer back to the things I discussed earlier. It’s not the end of the world, but you may be frustrated with the seemingly odd results you’re getting. While this is just a suggestion, it will make you look like a genius around your friends who don’t take the time to look up an easy-to-understand guide. Now, before we begin, here is your general disclaimer, enjoy! Read: how to overclock 1080ti
REFUSE!
WARNING! Overclock at your own risk. Overclocking a video card can void your warranty and cause other problems! OverclockersClub is not responsible for the information provided below. Please, if you have any questions, go to the forum and ask! Overclocking is at your own risk! Read: how to overclock 1080ti
Recommended software:
GPU-ZMSI AfterburnerHWMonitorUnigine Heaven Benchmark Read: how to overclock 1080ti
Each brand:
EVGA: EVGA Precision XOCZotac: FireStorm UtiltyMSI: MSI Afterburner Read more: How long does it take to freezeGigabyte: Xtreme Engine GamingASUS: GPU Tweak II
Video Tutorial:
For this tutorial, I decided to create an additional pair of videos. In the first video, I discuss NVIDIA Boost 3.0, which can be found in text just below this, and how it changes the playing field when overclocking. The second video only focuses on overclocking and how to do it with the MSI Afterburner software found on the second page. As always, if you found these videos helpful, be sure to leave some feedback and let us know how we’re doing! It is very important for us to create better content in the following articles. Read: how to overclock 1080ti Read: how to overclock 1080ti Read: how to overclock 1080ti
Learn NVIDIA GPU Boost 3.0:
NVIDIA has completely changed the way we think about overclocking with the third iteration of NVIDIA Boost technology – Boost 3.0. The idea that NVIDIA came up with was simple: to get the best performance without the consumer doing any footwork. The clock speed has traditionally been a linear design, in the sense that if you have frequency X the voltage should be Y. The linear number is projected on the board and can be thought of as a staircase with an interval certain space between each step. Each step will be a set frequency and voltage with nothing in between. In previous iterations, NVIDIA video cards would have three power states: one in idle, one in 2D, and one in 3D with set voltage and power parameters. Fast-forward to the current generation of Pascal GPUs and you have a completely different definition of what idle and 3D are. Gone are the common X and Y differences; In their place we have Boost 3.0, which allows the card to automatically change voltage and frequency based on a new set of parameters. These mainly revolve around Power Limit, Thermal Limit, and Voltage Limit, and you will hear these terms used quite often. These terms read like they are intended to do. Power Draw refers to the allowed power or total power draw of the video card. Thermal limiting refers to keeping the GPU in range so as not to damage the video card due to extreme heat. Finally, the Voltage Limit specifies the allowable voltage of the GPU. With all these safety features in mind, NVIDIA has implemented a setting that allows maximum performance to be achieved without users having to deal with the traditional overclocking woes that can potentially damage the video card. That clock speed is either unstable. Read: how to overclock 1080tiImage provided by Nvidia Read more: how to overclock 1080tiAlong with Boost 3.0 comes with some heavy restrictions from NVIDIA, which all ABPs (Authorized Partners) must comply with. While it’s nice to see out-of-the-box performance without user throttling, these limitations don’t help overclockers get the most out of their Pascal GPU. Each of the three parameters has its own disadvantages. NVIDIA locked the GPU to a maximum of 1,093v with no other work than to physically modify or own the EVGA K | NGP | N and use BIOS LN2. Read more: how to get free chat token without survey Second is the draw limit. not technically set by NVIDIA, but most video cards don’t allow over 120% of stock. Each vendor has 100% defaults usually in the 250 watt range. Because the GPU voltage is locked, no additional power is usually needed, as even with mild overclocking for gaming, these cards barely hit 110% at full load. Calculating workloads are a different story, as they tend to consume more power but offer lower stable load frequencies. However, according to my own observations NVIDIA has another set of parameters that are not listed, because even if the system is in a water cooling loop the frequency will drop for no reason other than a heavy workload. This leads me to conclude that there is an uncontrollable secret thermal limit. To make matters worse for longtime overclockers, the BIOS is encrypted, so the chances of a modified BIOS to remove these Boost features are slim. and Thermal Limit and increase the voltage to 1.24v max. Even if you don’t have an ASUS video card, you can flash the BIOS on most cards as they all have the same default parameters. I don’t recommend doing this as the performance gain is minimal for the risk you accept. You can overload the Founders Edition VRM fairly easily if you put it under an intense compute workload. N” crazy overclocks to 2600MHz, that’s because he’s using LN2 (liquid nitrogen) and has a lot of voltage mods applied. That in itself is not sustainable for everyday use. It is true that you will get a higher factory overclock with a custom PCB card, like the EVGA K | NGP | N or MSI Lighting Z, but with a little time you can get any card within reach of all the premium brands, as there is a limit to what you can achieve outside of LN2 . Read: how to overclock 1080ti
Stable system:
Before overclocking any component in your system, you must think about how much power the system will use. “How much electricity do I need?” is a common question all over the computer forums and really the answer is not a generic X amount. Make sure before overclocking anything, and just for the sake of computer components, that you have a good power source. This can be the difference between a stable computer and a poorly performing computer, or even a computer that is turned off during a gaming session. A quality power supply with lower wattage can go much further than an inexpensive, 1000 watt brand. I have seen it many times. Just because it’s labeled 1000 watts doesn’t mean it can sustain 1000 watts. A good brand and quality build will output its labeled quantity 24/7 without flinching. An easy way is to add each PCIe cable (6 pins or 8 pins) and the capacity provided by the motherboard. These cables are also known as PEG (PCI Express Graphics) cables. According to the specs, the motherboard should not provide more than 75 watts per PCIe slot, while the 6-pin PEG each provide 75 watts and the 8-pin PEG provides 150 watts. NVIDIA Founders Edition GTX 1080 Ti with a single 8-pin and 6-pin PEG connector must not use more than 300 watts at full load. The card doesn’t actually pull more than 220-260 watts, because of the voltage limitations explained in the Boost 3.0 section. NVIDIA lists the GTX 1080 Ti as a 265W Thermal Design Power (TDP) card, and in my own experience running two 1080Ti FE cards I’ve only seen 567 watts of power pull from the wall. This is not a guide, however, but I think most 600 watt power supplies should be able to handle a single card without any problems. That is unless you plan on going past the NVIDIA 1.093v specs. Read: how to overclock 1080ti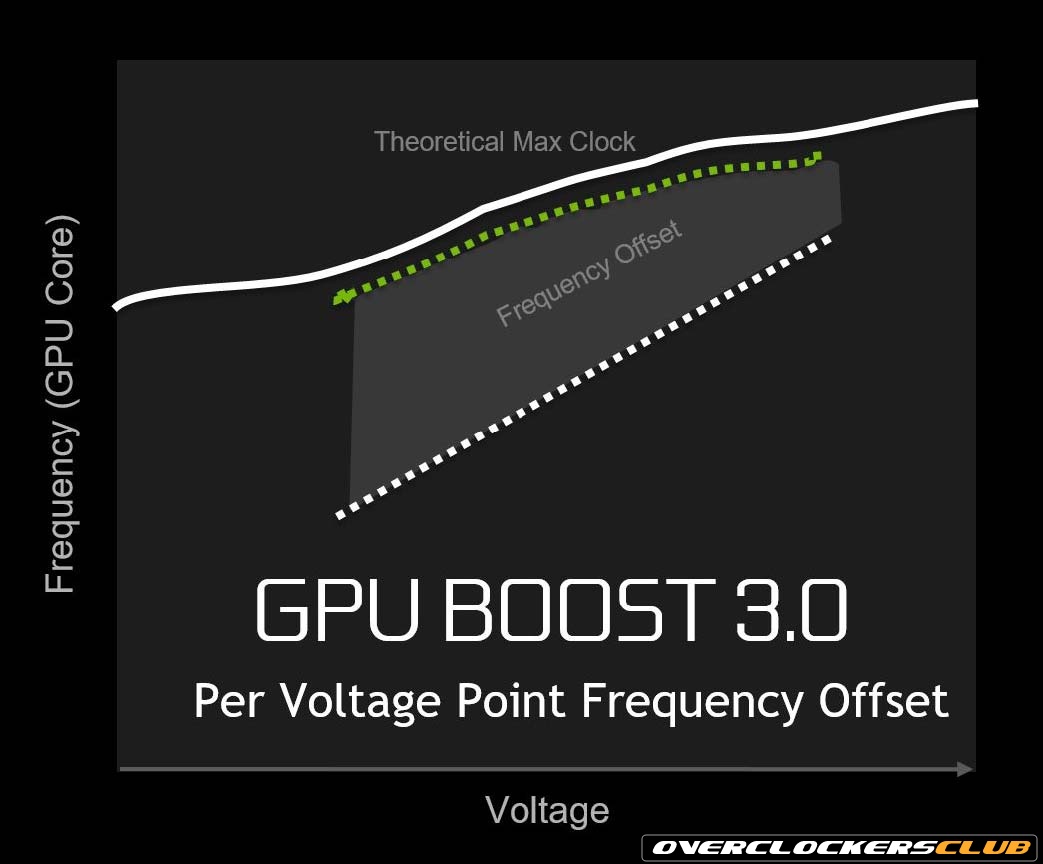
Overclocking ideas:
After a year of dealing with NIVIDA Boost 3.0 and previously writing a tutorial on the GTX 1070 OC, I can finally say that I have a solid understanding of how it works. Thinking about overclocking is still strange. It sounds confusing, but that’s what this guide is all about. As I explained above, this Boost 3.0 really throws a key into the system for veteran overclockers, since even your overclock will fail. It seems to be very snappy, and that’s something you’ll also encounter when tweaking your final overclock. I love the idea of NVIDIA giving every user a big advantage on what could be a low-performance stock card. This setting allows the video card to “overclock” itself while keeping the system within safe limits. In addition, most users will see clocks increase to 1850MHz for FE cards and 1950MHz for many non-reference video cards without having to do anything. Every brand has a fixed core and clock, though you’ll rarely see it that low. However that is the basic thing, because as above, if the card works unstable, it is not a big problem. The companies that make these video cards don’t say what speed it will run at. What we as overclockers are doing is just adding to the current boost number, which is quite confusing since not all cards perform equally. for many reasons, from thermal limitation, undervoltage, or power failure. As stated above, NVIDIA has locked the GTX 1080 Ti voltage down to 1,093v. It doesn’t matter what brand you have, you can’t go beyond this without hard modifications to the card. That means your max overclock can’t go past 2.2GHz because of the way Boost 3.0 works again with thermal, power, and voltage limitations. Most cards won’t go beyond 2012MHz for the 1080 Ti, as that’s the average I’ve come across while browsing through various forums. Remember, this is a very large GPU with 12 billion transistors in a small area. It’s hard to expect an overclock to be similar to a 1070 or even a 1080. Just remember, even if you can’t exceed what’s already offered, anything exceeds what the vendor lists. All of them are technically overclocked. Taking the 1860MHz Boost clock out of the box meant NVIDIA gave me a 270MHz boost overclock without even lifting a finger. As for my card and model, which is the EVGA 1080 Ti FE (Founders Edition), it doesn’t support anything higher than the 1582MHz boost clock listed specs, so please keep that in mind when overclocking your own card. Guide
Last, Wallx.net sent you details about the topic “NVIDIA GTX 1080 Ti Overclocking Guide❤️️”.Hope with useful information that the article “NVIDIA GTX 1080 Ti Overclocking Guide” It will help readers to be more interested in “NVIDIA GTX 1080 Ti Overclocking Guide [ ❤️️❤️️ ]”.
Posts “NVIDIA GTX 1080 Ti Overclocking Guide” posted by on 2021-10-21 10:15:07. Thank you for reading the article at wallx.net