How To Differentiate Between Streptococcus And Enterococcus
Video How to distinguish between streptococcus and enterococcus
Key Differences – Enterococcus and Streptococcus
Contents
Enterococcus and Streptococcus are two genera of bacteria, consisting of gram-positive, ovoid, and rod-shaped cells, respectively. Both of these bacteria are arranged in pairs or chains. Enterococcus tends to form short chains while Streptococcus mainly forms clusters but can be singly, in pairs or short chains. Both Enterococcus and Streptococcus can be found in the mucous membranes of animals. The Main difference between Enterococcus and Streptococcus is Enterococcus is a common gut microbiota while Streptococcus is a common upper respiratory tract microbiota.
Main areas covered
1. What is Enterococcus? – Definition, Structure, Pathology 2. What is Streptococcus? – Definition, Structure, Pathology 3. Similarities Between Enterococcus and Streptococcus – Outline of common features 4. What is the difference between Enterococcus and Streptococcus – Compare key differences Read: how to distinguish between streptococcus and enterococcus Key terms: Common Microbial, Enterococcus, Gram-positive bacteria, Mucous membrane, Streptococcus
What is Enterococcus?
Enterococcus refers to a group of bacteria that naturally occur in the intestines and cause inflammation and blood infections when introduced elsewhere in the body. It is an ovoid cell. Enterococci arranged in short strings. Some Enterococci are mobile. Enterococci have complex nutritional needs. Lactic acid is the main product of fermentation in Enterococci. In general, Enterococci are negative for catalase. However, some species produce pseudo-catalase. Catalase is an enzyme necessary for oxygen detoxification. In general, catalase-negative bacteria grow in an oxygen-free environment. Many Enterococci species tend to grow at 10°C. They can also grow at 65°C in the presence of 6.5% NaCl. Enterococcus infection in lung tissue is shown in figure 1. 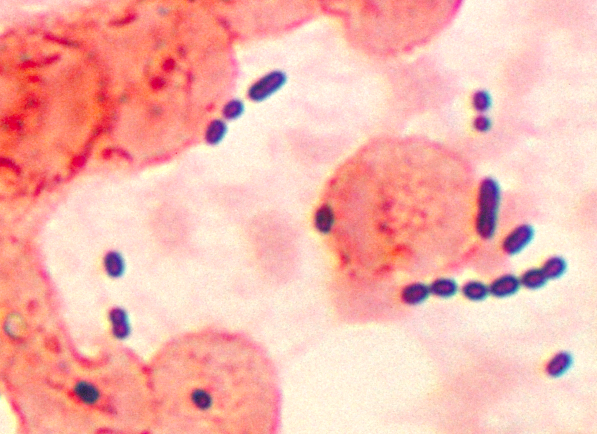
Pathology
Enterococci cause urinary tract infections, meningitis, bacteremia, bacterial endocarditis, and diverticulitis. They develop resistance to penicillin, ampicillin, and vancomycin. Therefore, new forms of antibiotics are introduced to inhibit the growth of Enterococci such as quinupristin-dalfopristin, linezolid, daptomycin, tigecycline.
What is Streptococcus?
Streptococcus refers to a group of bacteria that cause a multitude of diseases. It is a rod-shaped cell that shows an arrangement of clusters or short chains. In general, Streptococcus is not mobile. Streptococci are anaerobic bacteria that readily ferment lactic acid. Streptococcus is shown in figure 2. 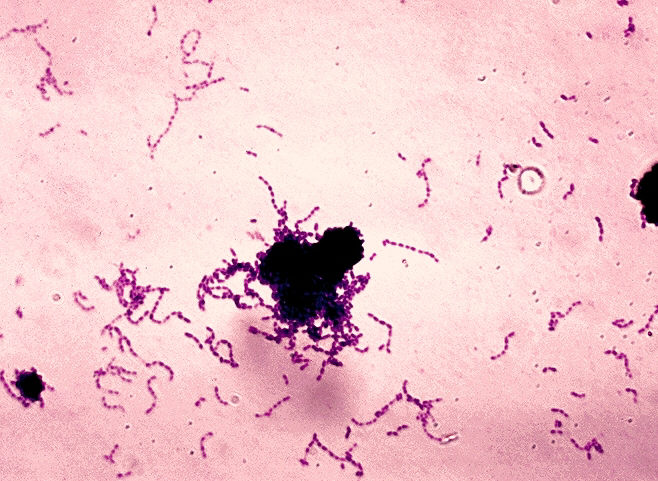
Pathology
Streptococcus causes hemolytic infections in red blood cells, pharyngitis, bacterial pneumonia, meningitis, endocarditis, … Penicillin is widely used to treat beta-hemolytic streptococci.
Similarities Between Enterococcus and Streptococcus
- Enterococcus and Streptococcus are two types of Gram-positive bacteria.
- Both of these bacteria are arranged in pairs or chains.
- Both Enterococcus and Streptococcus can be found in the mucous membranes of animals as adhesives.
- Some Enterococcus and Streptococcus are found in the soil.
- The long-chain fatty acids in the cell membranes of both Enterococcus and Streptococcus are either straight-chain or monounsaturated.
- Both Enterococcus and Streptococcus are non-reproductive, non-reproductive anaerobes.
- Both Enterococcus and Streptococcus undergo lactic acid fermentation.
- Both Enterococcus and Streptococcus were negative for catalase.
- Both Enterococcus and Streptococcus are pathogens that cause disease in humans.
What is the difference between Enterococcus and Streptococcus?
Definition
Read more: how to tie a fashionable turbanEnterococcus: Enterococcus refers to a group of bacteria that naturally occur in the intestines and cause inflammation and blood infections when introduced elsewhere in the body.Bridges: Streptococcus refers to a group of bacteria that produce the causative agents of sour milk, tooth decay, and hemolytic infections.
Shape
Enterococcus: Enterococcus is ovoid.Bridges: Cocci are rod-shaped.
Arrangement
Enterococcus: Enterococcus tends to form short chains.Bridges: Streptococcus mainly forms clusters but can be singly, in pairs or short chains.
Pyrrolidonyamplelamidase
Enterococcus: Most Enterococci species produce pyrrolidonyquerlamidase.Bridges: Pyrrolidonyamplelamidase is not produced by Streptococci.
Contents G + C
Enterococcus: The G+C content of Enterococci is ~38-45%.Bridges: The G+C content of Streptococci is ~33-46%.
Motivation
Enterococcus: Some species of Enterococci have the ability to move. Read more: how to make a motorcycle rackBridges: The bridge is not mobile.
Mucous membrane type
Enterococcus: Enterococcus is a common gut microbiota.Bridges: Streptococcus is a common upper respiratory tract microbiota.
Hemolysis
Enterococcus: Enterococcus does not cause hemolytic infections.Bridges: Streptococcus causes hemolytic infection.
Pathology
Enterococcus: Enterococcus causes inflammation and blood infection when introduced elsewhere in the body.Bridges: Streptococcus causes hemolytic infection.
Resistance to Penicillin
Enterococcus: Enterococcus develops resistance to penicillin.Bridges: Streptococcus is not resistant to penicillin.
Inference
Enterococcus and Streptococcus are two genera of gram-positive bacteria. Both types of bacteria are found in the mucous membranes of animals as a natural microbiome. Enterococcus is found in the upper respiratory tract while Streptococcus is found in the intestinal tract. The key difference between Enterococcus and Streptococcus is the type of mucous membrane of each bacterial genus. Hardie, JM and RA Whiley. “Classification and overview of the genera Streptococcus and Enterococcus.” Journal of Applied Microbiology, Blackwell Science Ltd, October 30, 2003, Available here. 2. “Intestinal infections.” Background, Pathophysiology, Epidemiology, January 2, 2018, Available here.3. “Streptococcal species.” Outline of Pathology – topqa.info, Available here. Image Courtesy: 1. “Histological pneumonia caused by Enterococcus 01” Image source: Content provider(s): CDC/Dr. Mike Miller – Cut from Media This is from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (PHIL) Public Health Image Library (Public Domain) via Commons Wikimedia2. “Streptococcus mutans 01” by PStreptococcus mutans on 4chan?
Last, Wallx.net sent you details about the topic “How To Differentiate Between Streptococcus And Enterococcus❤️️”.Hope with useful information that the article “How To Differentiate Between Streptococcus And Enterococcus” It will help readers to be more interested in “How To Differentiate Between Streptococcus And Enterococcus [ ❤️️❤️️ ]”.
Posts “How To Differentiate Between Streptococcus And Enterococcus” posted by on 2021-11-17 01:07:37. Thank you for reading the article at wallx.net