How To Calculate Delta G Of A Coupled Reaction
Combination reactions in biology
This is a common feature in biological systems, where some enzyme-catalyzed reactions can be understood as two combined half-reactions, one spontaneous and the other non-spontaneous. Organisms that normally hydrolyze ATP (adenosine triphosphate) to make ADVERTISEMENT (adenosine diphosphate) as spontaneous coupling reaction (Figure (PageIndex {1})).[ATP + H_2O rightleftharpoons ADP + P_i label{4}]Read: how to calculate delta g of a coupling reaction
- (P_i) is the inorganic phosphate ion
Read more: How to make wine in Florida Phosphoanhydride bonds formed by water repulsion between two phosphate groups of ATP exhibit large negative hydrolysis (-Delta G) and are therefore often referred to as “energy” bonds. high quality”. However, as with all bonds, energy is required to break these bonds, but the thermodynamic Gibbs energy difference is a strong “energy release” when thermodynamics are included. of phosphate ions; (Delta G) for this reaction is – 31 kJ/mol.Figure (PageIndex {1}): Hydrolyses ATP to form ADPATP which is the main ‘energy’ molecule produced by metabolism and it acts as a kind of ‘energy source’ in the cell: ATP is delivered wherever it is needed. a non-spontaneous reaction for two reactions to occur. coupled so that the overall reaction is thermodynamically beneficial.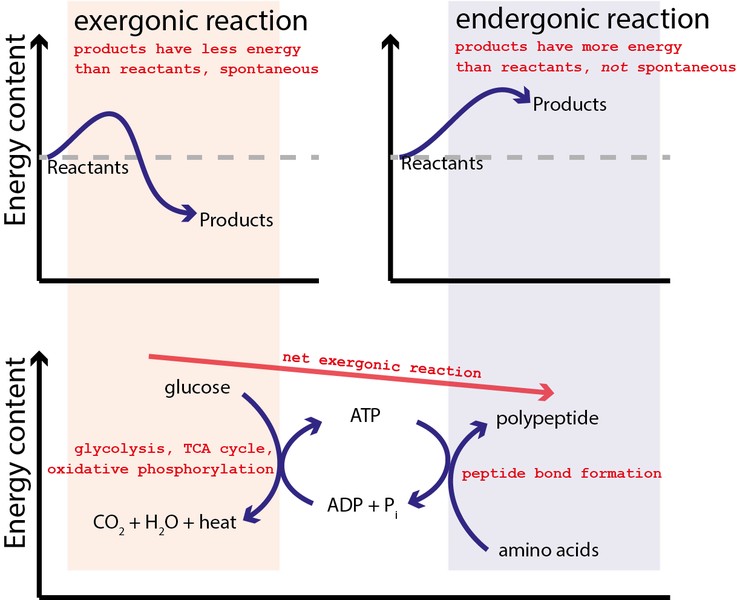
Last, Wallx.net sent you details about the topic “How To Calculate Delta G Of A Coupled Reaction❤️️”.Hope with useful information that the article “How To Calculate Delta G Of A Coupled Reaction” It will help readers to be more interested in “How To Calculate Delta G Of A Coupled Reaction [ ❤️️❤️️ ]”.
Posts “How To Calculate Delta G Of A Coupled Reaction” posted by on 2021-10-28 18:41:28. Thank you for reading the article at wallx.net