Distortion | Top Q&A
Accessed by: Effect > Distortion…
Type of deformation
Contents
These are profiling functions. Each type defines how the input signal is mapped to the output level. Each strain type has one or more control parameters that determine how the shaping function is applied. There are a total of five slider controls. The controls are turned on or off automatically depending on what “type” of distortion is selected. Read: how to distort sound.
shear deformation
Hard Clipping: This type of distortion cuts the peaks at the beginning and end of the waveform. Note that hard cutting is very prone to aliasing distortion, which can be undesirable.
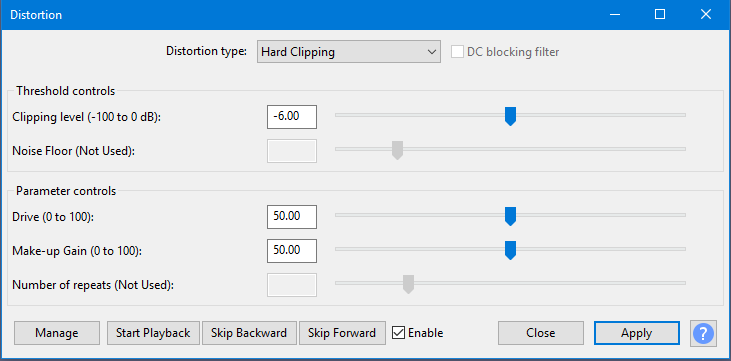
- Cutoff level (-100 to 0 dB): Peaks greater than this are clipped. The slider control has a logarithmic scale to allow settings close to 0 dB to be made more easily and accurately.
- Drive (0 to 100): When set to greater than 0, the waveform is amplified to this level (dB) before being clipped.
- Make-up Gain (0 to 100): When set greater than 0, the output from the effect is amplified. When set to 100, an amplifier such that an input level of 0 dB (full range height) will produce a 0 dB output level.
Soft Clipping This type of distortion is similar to Hard Clipping except that the ‘corners’ where the clip intersects with the waveform are rounded. This is achieved by gradually decreasing the gain when the input is above the cutoff threshold. The softer the cut, the rounder the cutting vertices and the less risk of aliasing distortion.
- Trim threshold (-100 to 0 dB): The level at which gain loss (trimming) begins. The slider control has a logarithmic scale to allow settings close to 0 dB to be made more easily and accurately.
- Hardness (0 to 100): ‘Hardness’ of the cut layer (100% is “hard”).
- Make-up Gain (0 to 100): When set greater than 0, the output from the effect is amplified. When set to 100, an amplifier such that an input level of 0 dB (full range height) will produce a 0 dB output level.
Note that even without “Make-up Gain”, the output level can be higher than the cutoff because the peaks are in effect flat rather than completely clipped.
Overdrive Distortion
Soft Overdrive This is the “softest” of the Overdrives and produces the fewest harmonics. It can be useful to reduce dynamic range (thus increasing the durability of the instruments) while adding the least amount of “cracking” to the sound.
- Amount of strain (0 to 100): The amount/intensity of the strain.
- Output level (0 to 100): Adjust the output level. When set to 0, the output will be silent.
Average Overdrive
- Amount of strain (0 to 100): The amount/intensity of the strain.
- Output level (0 to 100): Adjust the output level. When set to 0, the output will be silent.
Hard Overdrive Read more: how to fix an office chair that won’t hold This is the “hardest” of the Overdrives and produces the highest amount of harmonics. This is often used to create a heavily distorted effect.
- Amount of strain (0 to 100): The amount/intensity of the strain.
- Output level (0 to 100): Adjust the output level. When set to 0, the output will be silent.
Comedy distortion
Volume Curve (odd harmonics) This shaping function is often used in electric guitar distortion effects because aliasing distortion can be avoided with only an unduly small amount. This implementation uses no downsampling, although downsampling can be applied manually by resampling the track at a higher rate before applying this distortion effect. One limitation of this type of distortion is that even when fully applied, the effect is quite mild. A stronger effect can be achieved by applying the algorithm multiple times, which can be achieved by setting the “Repeat processing” control greater than 0. When applied only once, each frequency component of the tone The bar picks up a harmonic overtone 3 times the original frequency. When the effect is applied more than once, additional odd-numbered harmonics are generated.
- Amount of strain (0 to 100): The amount/intensity of the strain.
- Output level (0 to 100): Adjust the output level. When set to 0, the output will be silent.
- Iterative processing (0 to 5): The number of iterations of the distortion algorithm. When set to 0, the effect is applied only once.
Even Harmonics This type of distortion produces a series of harmonics with frequencies 2, 4, 6… times the frequency of the original waveform (even numbers). Generating uniform harmonics requires asymmetrically distorted waveforms, which, if left uncorrected, will produce significant DC offsets. To combat DC bias, a DC blocking filter is provided.
- DC blocking filter (check box) When selected, a low frequency filter is applied to reduce the DC component of the processed audio.
- Amount of strain (0 to 100): The amount/intensity of the strain.
- Harmonic Brightness (0 to 100): Higher values produce a larger number of harmonics.
Mixed deformation
Expansion and compression The transform shape for this type of distortion is an “S” sinusoid for both positive and negative signals. The distortion of high-pitched tones is similar to soft sound clipping or boost, while the distortion of low-level sounds is similar to crossover distortion.
- Amount of strain (0 to 100): The amount/intensity of the strain.
- Output level (0 to 100): Adjust the output level. When set to 0, the output will be silent.
Modeled deformation
Leveller Read more: how to get rid of musty smells in the garage This distortion is modeled on the “Leveler” (or “Leveler”) effect present in older versions of Audacity.
- Noise floor (-80 to -20): [default = -70] This is equivalent to the “Noise Threshold” setting in the original “Regulator” effect. It sets the noise threshold for the effect. For audio that isn’t already at full volume, higher threshold settings tend to amplify sounds at lower levels and can reduce the chance of background noise becoming annoying.
- Fine tuning (0 to 100): [default = 0] This is an additional control that is not available in the original effect. It allows fine adjustment of the amount of “leveling”.
- Level of upgrade (0 to 5): [default = 1] Level control is applied to the signal. When the fine adjustment is at 0, the values from 0 to 5 are equivalent to the original effect selections: 1 = Light, 2 = Medium, 3 = Heavy, 4 = Heavier, 5 = Heaviest.
Rectifier Distortion This type of distortion is simulated on a simple electronic component called a rectifier.
- DC blocking filter (check box) When selected, a low frequency filter is applied to reduce the DC component of the processed audio.
- Amount of strain (0 to 100): The amount/intensity of the strain. From 0 to 50% the bottom half of the waveform is clipped (hard clipping) until at 50%, only the top half of the waveform remains (equivalent to half-wave rectification. From 50 to 100%, the bottom half is left) of the waveform input is gradually reconstructed on the positive side (upper half) of the audio channel, until, at 100%, the waveform consists of the upper half plus the inverted lower half of the original waveform (equivalent to equivalent to full-wave rectification)
Hard Limiter 1413 This distortion is simulated on the LADSPA “Hard Limiter” plug-in that was included with older versions of Audacity. The default settings are different from the original effect (the initial default settings will not produce the effect).
- dB limit (-100 to 0dB): [default = -6] This is the amplitude level above which the input signal is processed. If the Wetness level is 100% and the Residue level is 0%, the resulting peak level will be truncated to this level.
- Wet level (-100 to 0dB): [default = 50] This is the percentage of the clipped signal being brought to the output. Therefore, it acts as a volume control for sounds below the dB limit. When set to 100%, all sounds below the dB limit will be fed into the output. At lower settings, the volume of the result will be reduced.
- Residue level (-100 to 0dB): [default = 50] This allows a proportion of the signal that has been removed by clipping to be added back to the output and thus softens the effect. When set to 0%, all clipped signals are discarded. At higher settings, some of the clipped signals will be restored, making the limit softer. Many peaks and troughs of the original waveform will be retained and the resulting volume level will be higher than what is set within the dB limit.
knot
Clicking the command buttons gives the following results:
- Manage provides a drop-down menu that allows you to manage the presets for the tool and view some details about the tool. For details, see Managing presets
- Start Playback start playback of the effect preview
- Skip Backward skips backward through the effect preview
- Skip Forward skips the transition through the effect preview
-
Enable preview listening with or without effects applied
- Apply apply effect to selected sound with current effect settings
- Close dialog box
takes you to the appropriate page in the Manual, this page
Factory presets
The factory presets included are:
- Default Factory default setting (Hard Clipping).
- Clip hard -12dB, increase brightness 80% Distortion that clip peaks at -12 db and then increase output level
- -12dB soft clamp, 80% makeup gain Same as the “Hard clamp” preset but with slightly rounded cutout for less aliasing.
- Fuzz Box A clipping effect commonly used with electric guitars.
- Radios A highly distorted effect suggestive of military radios. Can be used in conjunction with Filter Curve EQ or Graphic EQ effects for a more realistic walkie-talkie effect.
- The Blues drive maintains a Soft Acceleration Effect that boosts the volume of quiet sounds.
- Light Crunch Overdrive Medium/strong boost effect, reminiscent of the high input gain on a guitar amplifier.
- Heavy Overdrive Severe Distortion. “Turn it up to 11” type effect.
- 3rd tone (Perfect 5th) When applied to a sine tone, add a harmonic whose frequency is three times the frequency of the original tone.
- Van Overdrive A rather subtle overdrive effect with even harmonics. Harmonics whose frequency is an even multiple of the original frequency.
- 2nd tone (octave) When applying to sine tones, add a harmonic that is twice the frequency of the original tone (one octave above).
- Gated Extended Distortion Severely distorts both high and low level signals, making the peak parts much more “crispy” and quieter.
- Level Adjustment Levels, Light, -70dB Same as the “Level Leveler” effect that appeared in previous versions of Audacity.
- Leveling machine, moderate, noise floor -70dB
- Leveling machine, Heavy, noise floor -70dB
- Floor noise level, heavier, -70dB
- Floor noise level, heaviest, -70dB
- Half-wave rectifier Equivalent to a half-wave rectifier.
- Full-wave rectification Equivalent to full-wave rectification.
- Full-wave rectification (DC blocked) Equivalent to full-wave rectification with a high-pass filter to reduce DC . bias
- Percussion Limiter A stiff shear limiter that restores part of the clipped vertices to make distortion less severe. Can be effective for limiting peaks and adding “bites” to percussion sounds like trap drums and hi-hats.
Link
|
Last, Wallx.net sent you details about the topic “Distortion | Top Q&A❤️️”.Hope with useful information that the article “Distortion | Top Q&A” It will help readers to be more interested in “Distortion | Top Q&A [ ❤️️❤️️ ]”.
Posts “Distortion | Top Q&A” posted by on 2021-08-30 21:45:15. Thank you for reading the article at wallx.net
 Enable preview listening with or without effects applied
Enable preview listening with or without effects applied