Why Do Helium Balloons Deflate So Fast?
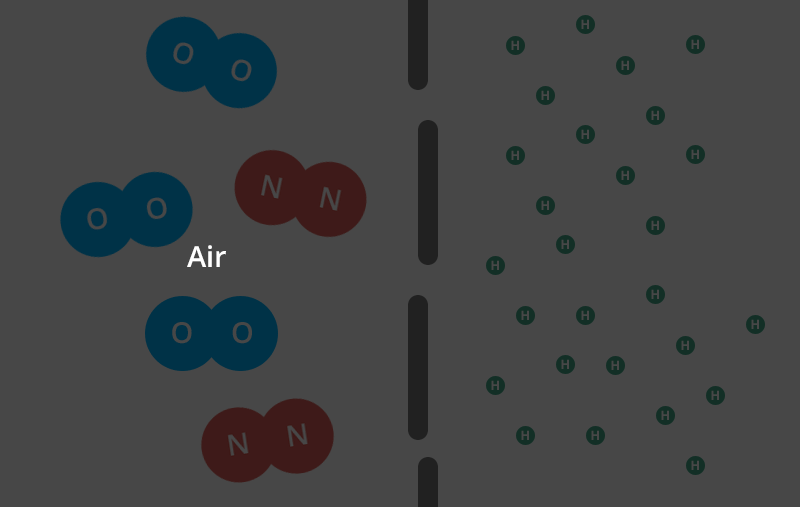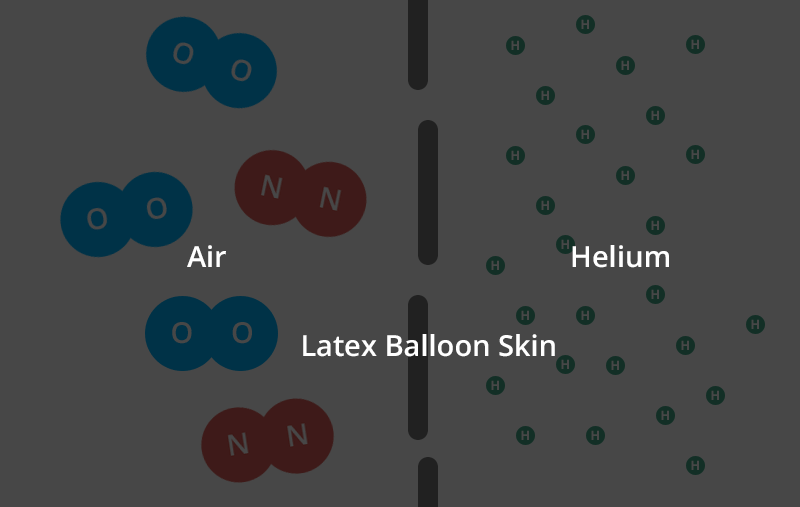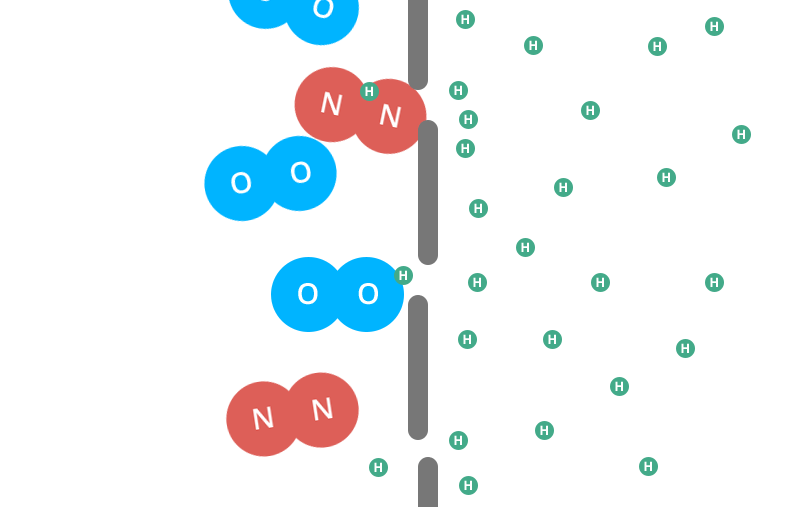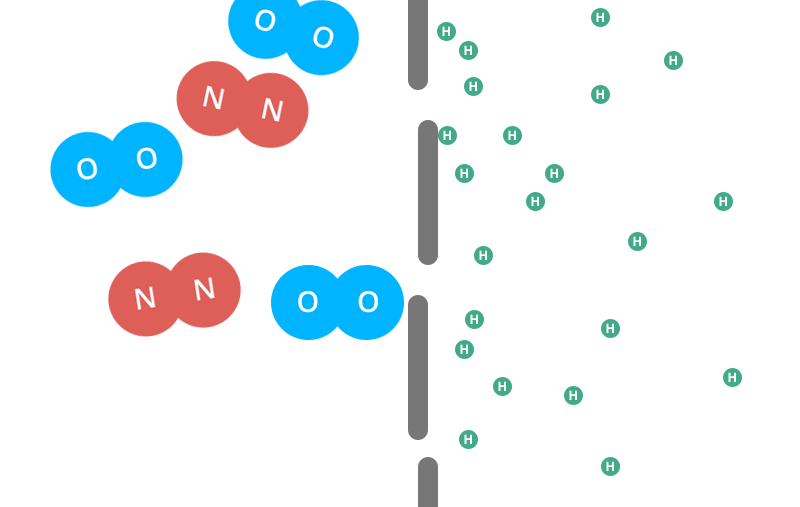
Helium balloons deflate faster than air balloons and rubber balloons faster than foil. But why do helium balloons deflate? Find out here. There are actually a few different factors that come into play here. Let’s start with the rubber balloon. Read: why do balloons deflate If you magnify the balloon enough times to see its structure, you’ll see what looks like a pile of noodles. And like a pile of noodles, in between those tiny fibers you’ll notice thousands of tiny gaps.That’s right — your rubber ball is full of holes! (And when you inflate the balloon and stretch the latex, you open the holes wider.) Now, these holes are extremely small. Remember, you are looking through a microscope. But over time, the air or helium inside the balloon will escape from the porous walls and you will be left with your deflated balloon. This is called “osmosis”. However, you may find that your helium balloons take a long time to fail while your air-filled rubber balloons are still inflated. really. And we’re not talking about hot air balloons, Hyli is the second smallest molecule on the periodic table. The individual oxygen and nitrogen molecules (the air in your air-filled balloon) are about four times larger than the helium molecules. In the gaseous form, each helium molecule moves around on its own. The oxygen and nitrogen molecules are diatomic in nature, meaning they are bonded together in pairs. That means these conjoined molecules are now almost eight times larger than a single helium molecule. Next, the two adults linked arms and passed through the same door parallel to each other. Two adults will have a harder time getting through the door than a small child. This is what happens with different molecules.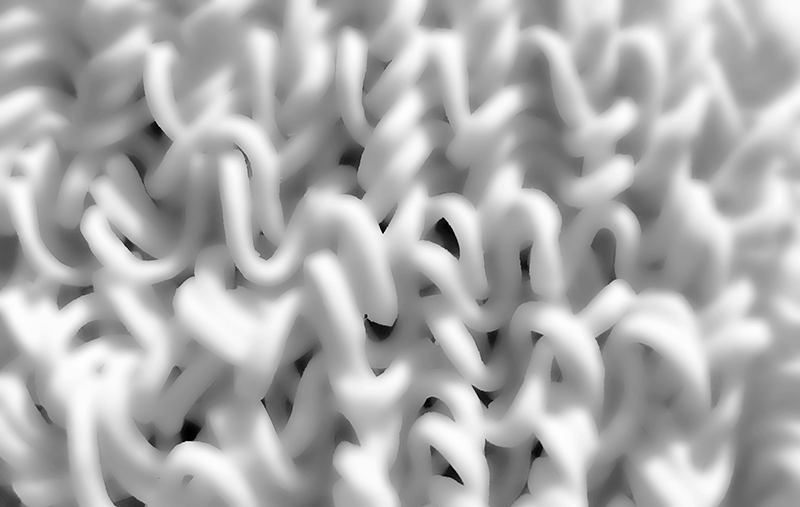
Last, Wallx.net sent you details about the topic “Why Do Helium Balloons Deflate So Fast?❤️️”.Hope with useful information that the article “Why Do Helium Balloons Deflate So Fast?” It will help readers to be more interested in “Why Do Helium Balloons Deflate So Fast? [ ❤️️❤️️ ]”.
Posts “Why Do Helium Balloons Deflate So Fast?” posted by on 2021-09-02 04:42:15. Thank you for reading the article at wallx.net