How To Make Drumsticks For Drums
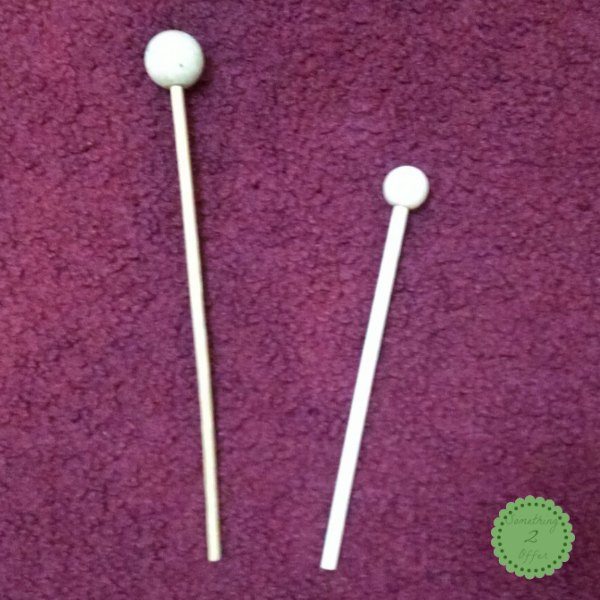
Today we join Thaleia for the 2nd Offer as part of our 5 Senses Challenge. Here’s how to make a quick and easy homemade drumstick and drumstick. Thaleia writes about homeschooling and raising four highly motivated students from 1 and a half to 12 years old. Their latest adventure is dealing with type 1 diabetes and all that. She is always creatively distracted but has a heart to find the frugal activities that have fed her family. If you like American History, check out ABC’s American History series Tuesday through June. Offer 2 continues our Hearing week. — Reading: how to make drumsticks I am happy to be here today to share about our homemade drums and sticks. Since we are homeschooling on a very tight budget, I try to find fun and budget-friendly things all year round for my kids. A few years ago, our local park held Day Camps. Each week is a different theme including Art and Music.I signed both Eldest and Princess in a split second. Every morning they went camping for 3 hours and had a great time. They make some very unique items every day, and at the end of the week, they’ll display those items on Family Day. My kids enjoyed this camping week so much that they signed up again for next Summer so we now have 4 very unique but easy-to-empty items. And of course if you have a drum you’ll need a drumstick!



Last, Wallx.net sent you details about the topic “How To Make Drumsticks For Drums❤️️”.Hope with useful information that the article “How To Make Drumsticks For Drums” It will help readers to be more interested in “How To Make Drumsticks For Drums [ ❤️️❤️️ ]”.
Posts “How To Make Drumsticks For Drums” posted by on 2021-10-28 02:01:28. Thank you for reading the article at wallx.net