Reagent Friday: Lithium Di-isopropyl Amide (LDA)
Video What is lda Organic Chemistry?Lithium Diisopropyl Amide (LDA), A Solid, Obstructed BaseIn an obvious addition to the Reagent Guide, every Friday I profile a different reagent commonly encountered in Organization 1 / Organization 2. Version 1.2 was released just last week, with a bunch of tweaks and a new page index. organic chemistry ldaIf NaNH2 is a piranha, then today’s reagent – lithium diisopropylamide (LDA) is like a hammerhead shark. It also has a strong bite, but that particular proboscis can get in the way. So LDA can’t approach tight spaces in the same way that NaNH2 can.
Formation of Enolates Less Obstructed (“Kinetic”) With LDA
Contents
In other words: The LDA is a sturdy, bulky stand. The most common use of LDA is in the formation of enolate. In the example below, notice how both atoms with the C=O bond have a CH bond? LDA will selectively remove the proton from the carbon being replaced with the least amount of carbon: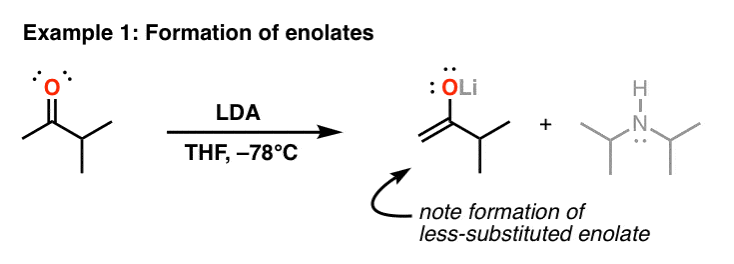
Alkylation, halogenation and aldolization of enolates obtained with Lithium Diisopropylamide
Why is LDA useful? Well, enolate is extremely useful ndrinker, which can participate in SN2 reactions with alkyl halides as well as aldol reactions (among many others). If we use NaNH2 to form an enolate like this, we might get mixture of two enolates, will give a mixture of products. LDA’s selectivity for the formation of the less-substituted enolate makes it extremely useful.
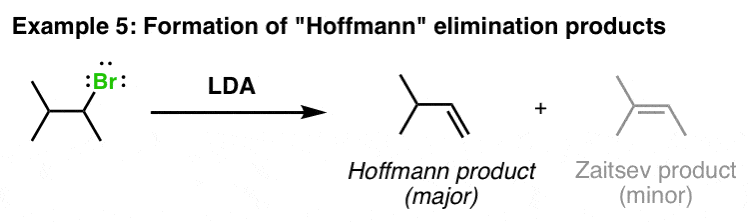
Formation of less substituted Alkenes (“Non-Zaitsev” or “Hoffmann”) in elimination reactions
Although less common, LDA can also be used to form the “Hoffman” product in exclusion reactions. The usual basis for this is potassium t-butoxide, but LDA can do that too:
Formation of less substituted enolates with LDA: Mechanism
How it works: The diagram below shows the reaction between LDA and ketones. Note the forming bonds (NH, CC) and breaking bonds (CH, CO). The resulting enolate has a resonance isomer in which a negative charge is on the carbon. This is in some respects the more “important” form of resonance, since carbon tends to be a better nucleophile than oxygen in enolate reactions. Read more: What is endurance in league of legends.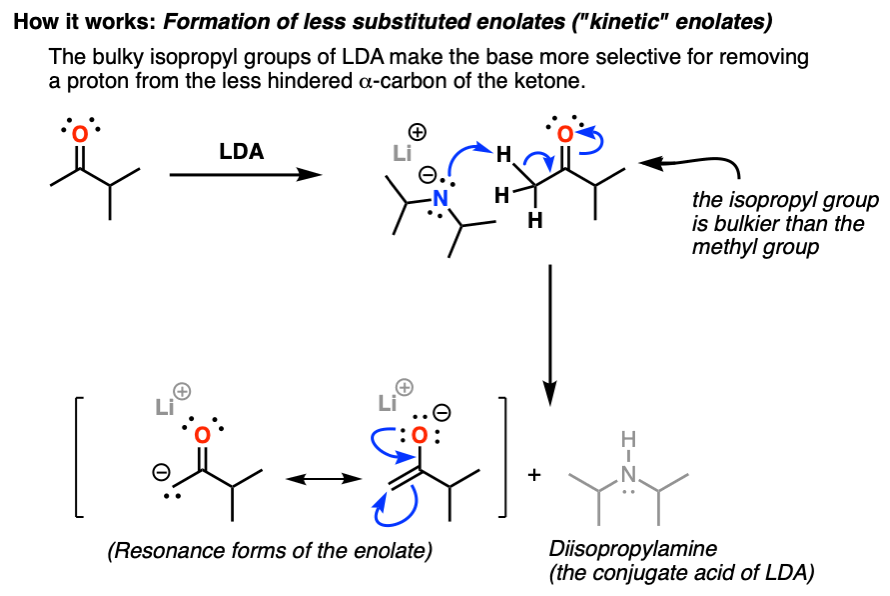

Read more: what is the square root of 69 | Top Q&A
Last, Wallx.net sent you details about the topic “Reagent Friday: Lithium Di-isopropyl Amide (LDA)❤️️”.Hope with useful information that the article “Reagent Friday: Lithium Di-isopropyl Amide (LDA)” It will help readers to be more interested in “Reagent Friday: Lithium Di-isopropyl Amide (LDA) [ ❤️️❤️️ ]”.
Posts “Reagent Friday: Lithium Di-isopropyl Amide (LDA)” posted by on 2021-08-21 20:24:05. Thank you for reading the article at wallx.net