Where is sugar removed from the blood
Video Where to Remove Sugar from the Blood While this course is primarily created for healthcare professionals to assist in cutting down on issues associated with insulin prescribing and administration, we hope that the people with diabetes who do not have access to a medical professional and who need to learn more about how insulin works.
Important data
Contents
How is glucose produced? Glucose is made by breaking down carbohydrates, mainly in the small intestine, after we eat a meal containing carbohydrates (reminiscent of pasta or bread). When fasting our blood sugar is usually around 4.5-5.5 mmol/L however this can rise to 7 mmol/L or higher when consumed but it should return to normal within 2 hours of consumption. Glucose cannot cross cell membranes without using carrier proteins, and insulin is needed to facilitate the removal of glucose from the blood stream for it to enter cells. go in the glycogen category during insulin stimulation. Glycogen is an extremely branched structure, made up of many glucose molecules linked together. When required, glycogen is simply and rapidly broken down again to form glucose. Read more: where are you going, where have you been | Top Q & AGlycogen is stored specifically in the liver (where it makes up 10% of the liver’s weight and will be returned to the bloodstream) and muscles (where it can be converted back to glucose but used only). by muscles). As a result, excess glucose stays far away from the blood stream and is stored.
At a greater depth
Glucose uptake by tissues
Glucose cannot cross cell membranes without using transport proteins. We will mainly think about the glucose transport protein GLUT 4. Take a look at the diagram below. In the left diagram, there is no such thing as insulin flow so Glut 4 is still stored in the cells and glucose is introduced into the blood in low amounts using Glut 1 or 3. In the best hand diagram, the scene insulin tells the cell to translocate Glut 4 into the cell membrane. Now large amounts of glucose will be introduced into the cell, via the Glut 4 transporters, in addition to the low range via Glut 1 or 3. Insulin is essential for this approach.Determination: insulin stimulates translocation of Glut 4 to the membraneGLUTs 1 and 3 now take up basal glucose, which means the cell has always been able to absorb low amounts of glucose. However, GLUT 4 is insulin sensitive (muscle or fat cells). That means that after we eat, glucose regulates insulin and binds insulin to the insulin receptor ending up following the movement of GLUT 4 from the intracellular granules to the cell membrane, allowing the cell to absorb a large glucose. Due to this fact, glucose stays far away from the blood stream and enters cells.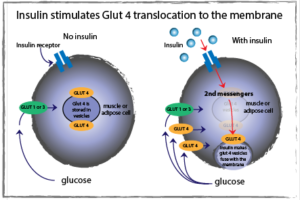
Store glucose in the form of glycogen
Read more: Where to buy a scaevan device As glucose levels increase, the body stores it as glycogen in a process stimulated by insulin. Glycogen is an extremely branched structure, made up of many glucose molecules linked together. When required, glycogen is simply and rapidly broken down again to form glucose. Read more: where are you going, where have you been | Top Q & AGlycogen is stored specifically in the liver (where it makes up 10% of the liver’s weight and will be returned to the bloodstream) and muscles (where it can be converted back to glucose but used only). by muscles). As a result, excess glucose stays far away from the blood stream and is stored.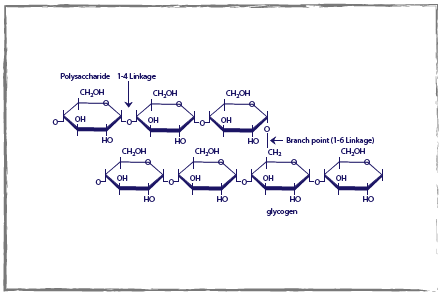
Metabolizing glucose to generate ATP by glycolysis and the Krebs cycle
Glucose enters the cell where it undergoes phosphorylation to glucose-6-phosphate. The conformational change of glucose means that glucose cannot be transported again outside the cell, and the cells feel that the focus of glucose on the outside of the cell is greater than on the inside. Thus, they maintain glucose transport into cells, leading to a decrease in blood glucose levels. Once stored in the cytoplasm, glucose enters the glycolysis pathway. This is a multi-step pathway that ends in the technology of two ATPs, and is managed in part by insulin and glucagon. ATP technology is essential for the body, because it is the principle that gives vitality to the cells. The leading product of the fecal pathway is acetyl coA. This molecule can then participate in the Krebs Cycle in mitochondria, which produces 36 ATPs, making it the base generator of the cell in most cases. Therefore, the body metabolizes glucose to generate vitality. Read more: Where to stay in Hvar: 10 best regions | Top Q&A
Last, Wallx.net sent you details about the topic “Where is sugar removed from the blood❤️️”.Hope with useful information that the article “Where is sugar removed from the blood” It will help readers to be more interested in “Where is sugar removed from the blood [ ❤️️❤️️ ]”.
Posts “Where is sugar removed from the blood” posted by on 2022-04-11 09:37:24. Thank you for reading the article at wallx.net






