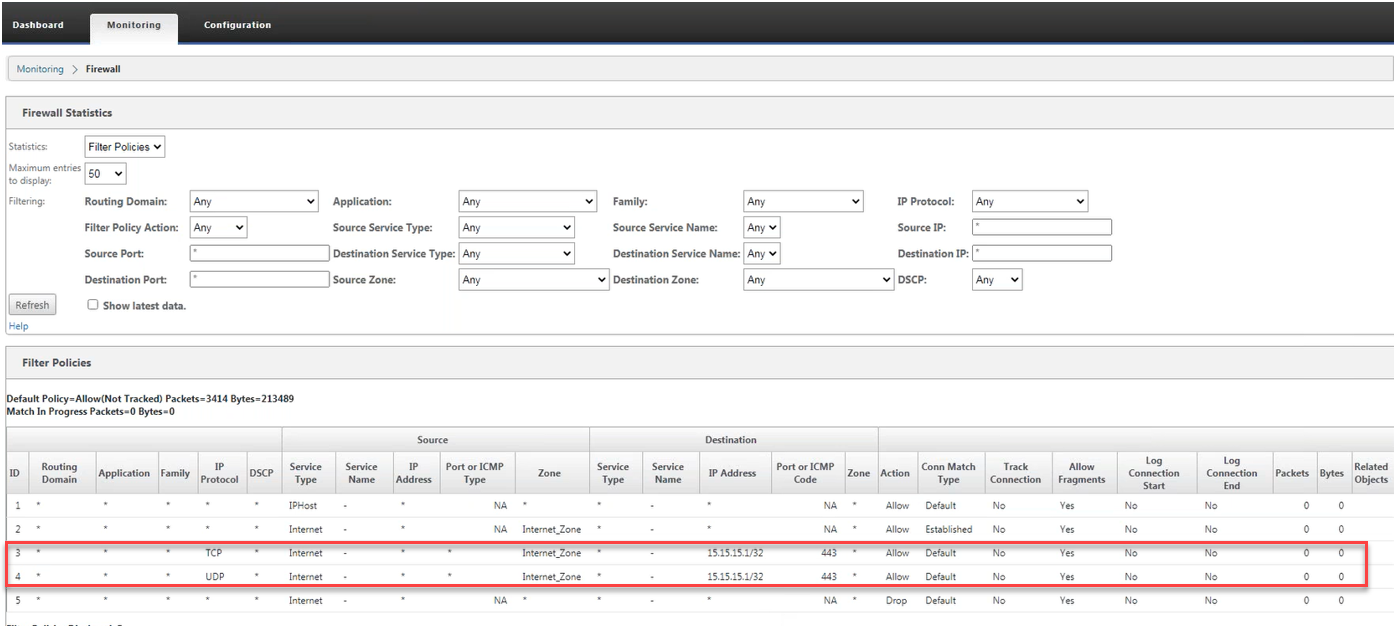
Dynamic NAT
Dynamic NAT NATDynamic is a many-to-one mapping of a private IP address or subnets inside an SD-WAN to a public IP address or subnet outside of the SD-WAN. Traffic from different zones and subnets over trusted (internal) IP addresses in the LAN segment is sent over a public (external) IP address.
Types of Dynamic NAT
Contents
Dynamic NAT performs port address translation (PAT) along with IP address translation. Port numbers are used to distinguish which IP address the traffic belongs to. A single public IP address is used for all internal private IP addresses, but a different port number is assigned to each private IP address. PAT is a cost-effective way to allow multiple servers to connect to the Internet using a single Public IP address.
- Ports are restricted: Port-restricted NAT uses the same external port for all translations related to the internal IP Address and port pair. This mode is commonly used to enable P2P Internet applications.
- Symmetry: Symmetric NAT uses the same external port for all translations related to Internal IP Address, Internal Gateway, External IP Address, and External Gateway tuple. This mode is often used to increase security or extend the maximum number of NAT sessions.
NAT at home and abroad
Connection direction can be from inside to outside or from outside to inside. Once a NAT rule is created, it will be applied to both directions depending on the direction match type.
- Going abroad: Translated destination address for packets received on the service. The source address is translated for packets transmitted on the service. Dynamic outbound NAT is supported on local domain services, Internet, Intranet and Inter-routing domain. For WAN services such as Internet and Intranet services, the configured WAN link IP address is dynamically selected as the external IP address. For local domain and interrouting domain services, provide the external IP address. The Outer Zone is derived from the selected service. A typical use case of external dynamic NAT is to allow multiple users on your LAN to securely access the internet simultaneously using a Public IP address.
- Arrive: Translated source address for packets received on the service. The destination address is translated for packets transmitted on the service. Incoming dynamic NAT is not supported on WAN services such as Internet and Intranet. There is an obvious audit error to indicate the same thing. Incoming dynamic NAT is only supported on local and interrouting domain services. Provide the external zone and the external IP address to be translated to. A typical use case for inbound dynamic NAT is allowing external users to access email or web servers hosted in your private network.
Configure dynamic NAT policy
To configure dynamic NAT policies, in the Configuration Editor, navigate to Connection > Firewall > Dynamic NAT policy.
- Priority: The policy order is applied in all defined policies. Lower priority policies are applied before higher priority policies.
- Direction: The direction the traffic is flowing, from the perspective of the virtual interface or service. It can be inbound or outbound traffic.
- Type: Type of Dynamic NAT to perform, Port Restricted or Symmetrical.
- type of service: Type of SD-WAN service to which the dynamic NAT policy is applied. Incoming dynamic NAT is supported on interrouting domain and local domain services. External dynamic NAT is supported on local domain services, Internet, Intranet and Inter-routing domain
- service name: Select the configured service name corresponding to the Service Type.
- Inner area: Inner firewall zone match type to which the packet must go to allow translation.
- Outside area: For incoming traffic, specify the external firewall zone match type the packet must go to to allow translation.
- Internal IP address: The internal IP address and prefix must be translated if the match criteria are met. Type ‘*’ to indicate any internal IP address.
- External IP address: The outer IP address and the prefix to which the internal IP address is translated if the matching criteria are met. For outbound traffic using Internet and Intranet services, the configured WAN link IP address is dynamically selected as the external IP address.
- Allow related: Allow flow-related traffic that matches the rule. For example, a thread-specific ICMP redirect is compliant with the policy, if there’s some sort of stream-related error.
- IPsec pass through: Enable IPsec (AH/ESP) interpretation.
- GRE / PPTP pass through: Enable GRE/PPTP interpretation.
- Port parity: If enabled, external ports for NAT connections maintain parity (even if internal port is even, odd if external port is odd).
- Constraint on responder route: Make sure that the response traffic is sent through the same service it was received from, to avoid asymmetric routing.
Port forwarding
Dynamic NAT with port forwarding allows you to forward specific traffic to a specific IP address. This is usually used for internal servers like web servers. Once dynamic NAT is configured, you can define port forwarding policies. Configure dynamic NAT for IP address translation and define port forwarding policies to map external ports to internal ports. Dynamic NAT port forwarding is commonly used to allow remote hosts to connect to hosts or servers on your private network. For a more detailed use case, see Citrix SD-WAN Dynamic NAT explained.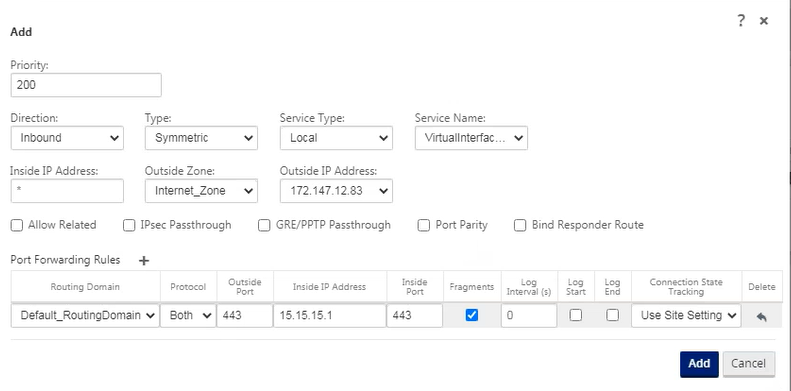
Dynamic NAT policy is automatically generated
Dynamic NAT policies for Internet services are automatically generated in the following scenarios:
- Configure internet service on untrusted interface (WAN link).
- Enable internet access for all routing domains on a WAN link. For more details, see Configure firewall segments.
- Configure a DNS forwarder or DNS proxy on the SD-WAN. For more details, see Domain Name System.
Monitoring
To monitor dynamic NAT, navigate to Monitoring > Firewall statistics > Connection. For a connection you can see if NAT has been performed or not.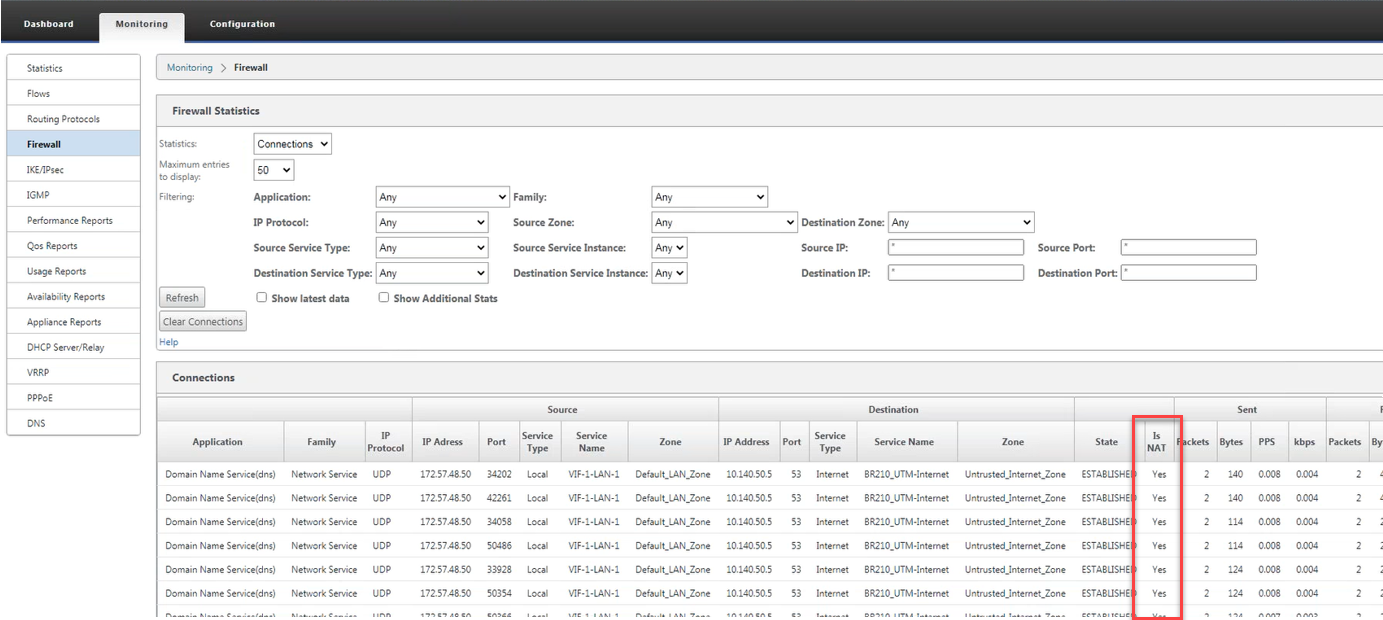
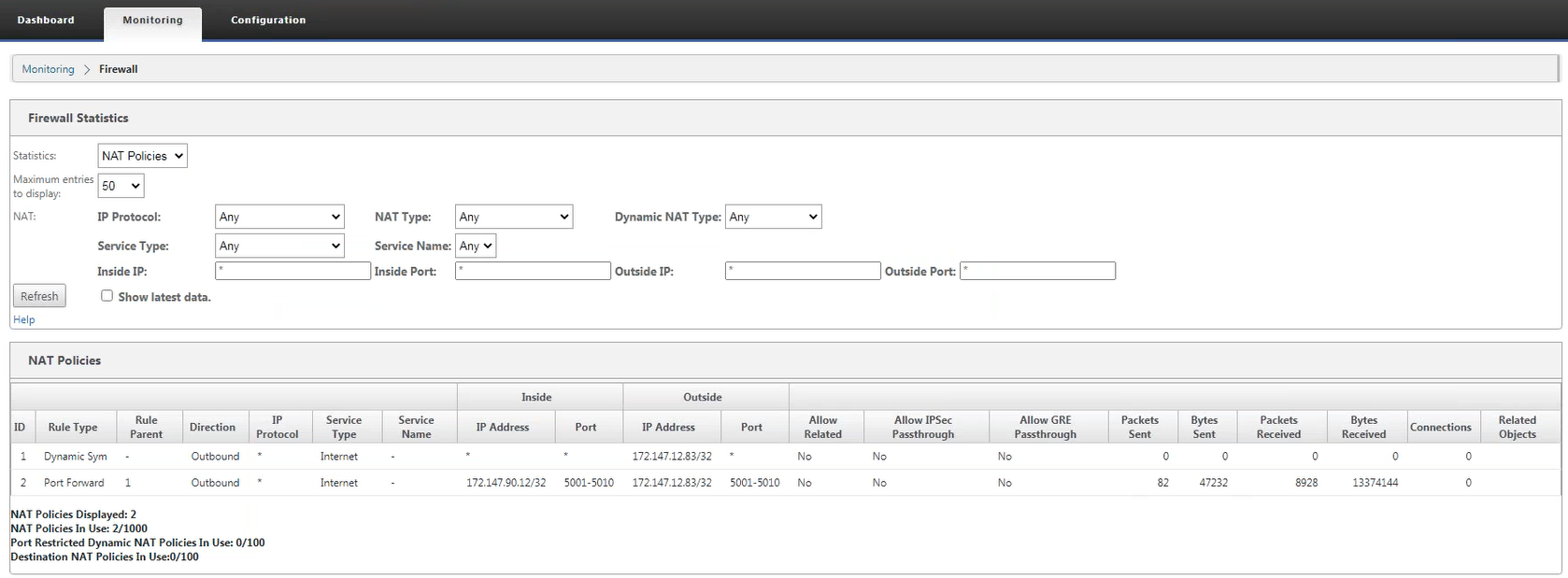
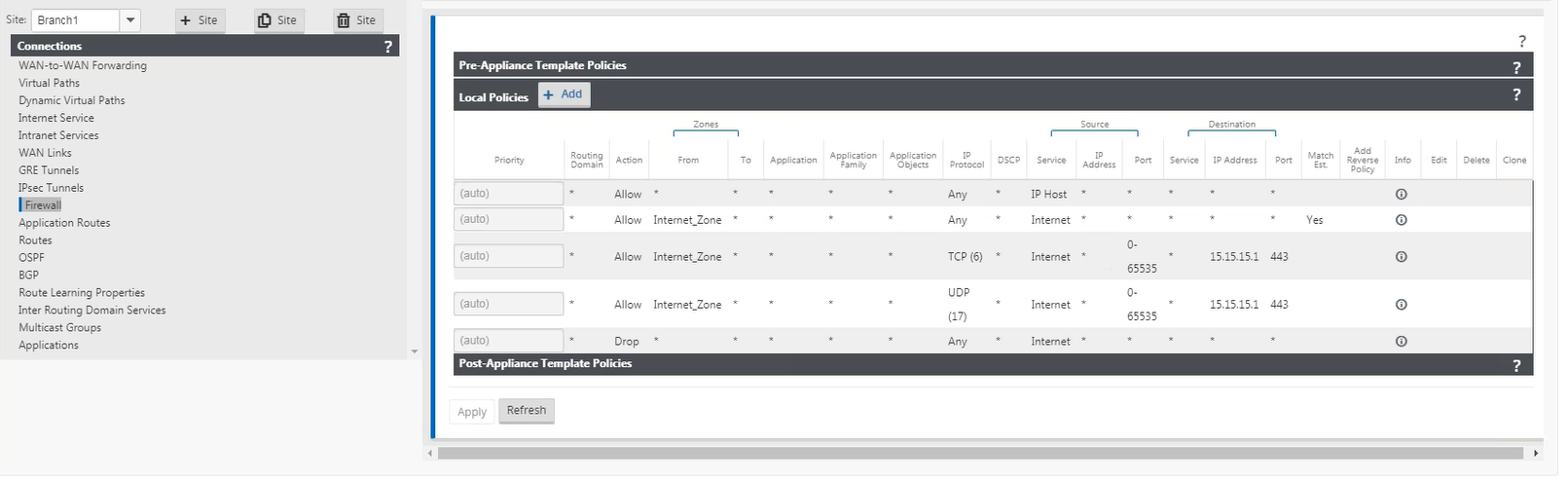
Diary
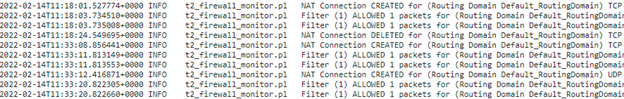
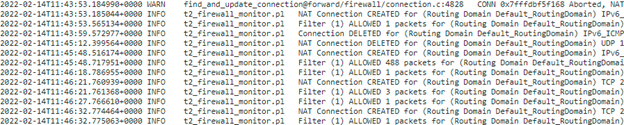
You can see NAT related logs in the firewall log. To view logs for NAT, create a firewall policy that matches your NAT policy and ensure that logging is enabled on the firewall filter.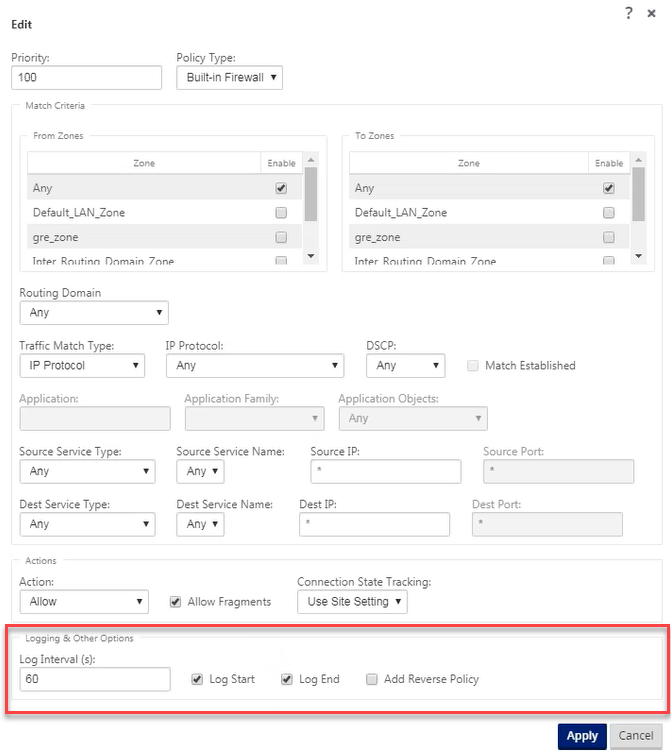
Last, Wallx.net sent you details about the topic “Dynamic NAT❤️️”.Hope with useful information that the article “Dynamic NAT” It will help readers to be more interested in “Dynamic NAT [ ❤️️❤️️ ]”.
Posts “Dynamic NAT” posted by on 2021-08-17 08:10:06. Thank you for reading the article at wallx.net